 Temperature imaging of submillimeter-thick aqueous solution using near-infrared
spectroscopy Temperature imaging of submillimeter-thick aqueous solution using near-infrared
spectroscopy
It is impossible for infrared (IR) imaging, so called thermography, to obtain temperature images of aqueous solutions inside a microchip because IR radiation from the liquid is overwhelmed by radiation from the microchip’s materials such as glass and poly-dimethyl siloxane (PDMS). In addition, IR imaging is a passive method, which means that signal intensity from a micro-area would become too small to be detected. Our study presents a novel method for temperature imaging using near-infrared light. The principle is based on the temperature dependence of the absorption band of water. This method would be useful for temperature measurement applications and control of aqueous solutions in microchips.
Keywords: Temperature imaging, Aqueous solution, Near-infrared spectroscopy, Microchip.

Figure: Temperature image of 0.5 mm-thick water heated by a nichrome wire
with a diameter of 0.05 mm.
more information
 Temperature dependence of infrared absorption spectrum of thin-film water Temperature dependence of infrared absorption spectrum of thin-film water
Infrared spectroscopy (IRS) is a noncontact method to measure solute concentration,
water content, and temperature of aqueous solutions. To apply IRS to microchip
analyses, it is important to investigate the characteristics of IR absorption
of extremely thin water, which must be different from that of bulk water.
Since water strongly absorbs mid-infrared light (wavelength from 2500 nm
to 5000 nm), an attenuated total reflection (ATR) method is commonly used
in spectral analyses. However, our study focuses on a transmission method,
considering usability with existing microchips and the development of imaging.
Keywords: Infrared spectroscopy, Thin-film water, Temperature, Microchip.
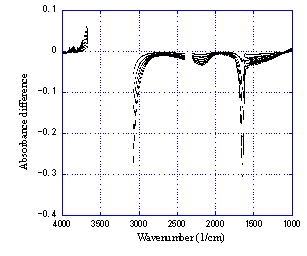
Figure: Temperature dependence of mid-infrared absorption spectrum of 10 µm-thick water.
more information
 Applications of corona discharge at the tip of a micropipette electrode Applications of corona discharge at the tip of a micropipette electrode
Micropipette electrode is a glass micropipette coated with metal film.
When high voltage (1-2 kV) is applied to the electrode in atmospheric air,
corona discharge occurs from the tip to a counter plate electrode. Although
the corona discharge takes low electric power, strong electric field is
formed in the vicinity of the tip, which could decompose or ionize various
substances.
Keywords: Micropipette electrode, Corona discharge, Microplasma.

Figure: SEM image of the tip of a micropipette electrode. The tip diameter
is 1 um. The surface (except the tip) is coated with diamond-like carbon
for electrical insulation.

Figure: glow corona at the tip of a micropipette electrode in atmospheric
air.
more information
 Cellular measurement using micropipette electrodes Cellular measurement using micropipette electrodes
Keywords: Cell, Micropipette, Electrometry, Injection.
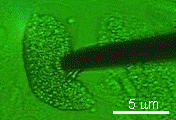
Figure: micropipette electrode and cell.
more information
 Imaging of water content inside and outside cells Imaging of water content inside and outside cells
Keywords: Water, Absorption, Spectroscopic imaging, Cell membrane.
more information
 Biomedical applications of ion beam Biomedical applications of ion beam
Keywords: Ion beam, Atmosphere, Biological application
more information
Page's top
October 6, 2008 Update |

